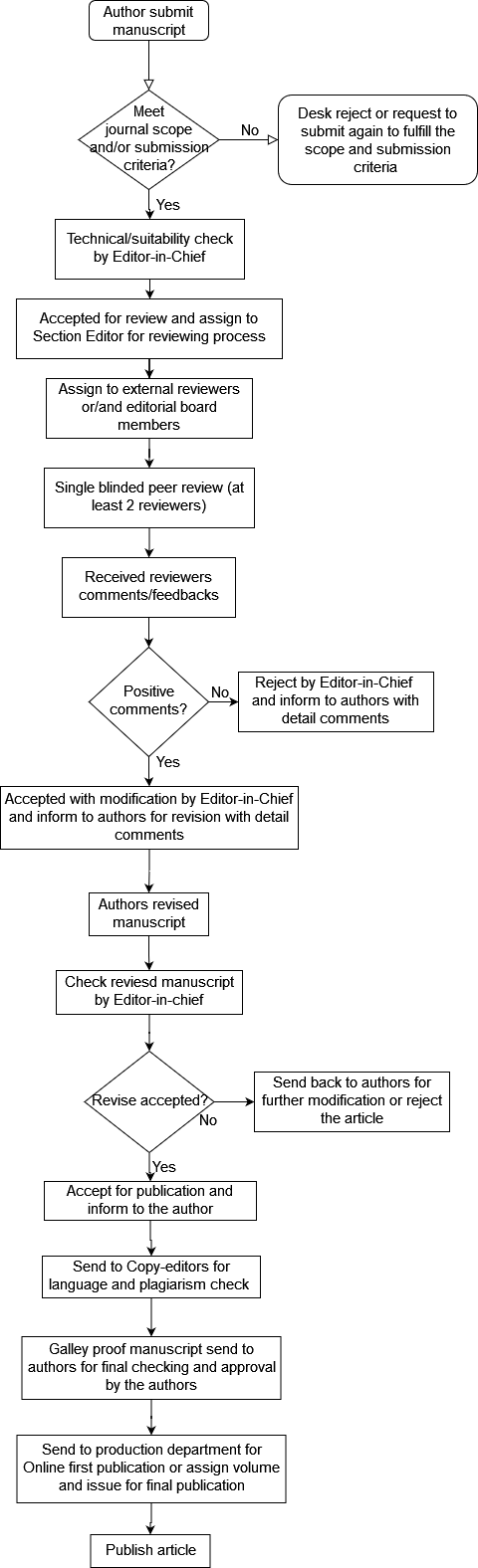
Publication Process
Published articles in peer-reviewed journals are essential for developing an organized and respected system of knowledge. Peer review is crucial for maintaining high standards in academic publication. The Disaster in Civil Engineering and Architecture Journal uses a single-blind (single anonymized) peer review process to evaluate submitted manuscripts. In this type of review, the identities of the reviewers are not disclosed to the authors.
All contributions will be initially assessed by the editor for suitability for the journal. Papers deemed suitable are then typically sent to a minimum of two independent expert reviewers to assess the scientific quality of the paper. The Editor is responsible for the final decision regarding the acceptance or rejection of articles. The Editor's decision is final. Editors are not involved in decisions about papers that they have written themselves or have been written by family members or colleagues or which relate to products or services in which the editor has an interest. Any such submission is subject to all the journal's usual procedures, with peer review handled independently of the relevant section editors.
Independent Reviewers are asked to evaluate the quality of the manuscript and to provide a recommendation on whether a manuscript can be accepted, requires revisions, or should be rejected. Peer review of a submitted manuscript is carried out while keeping in mind the scope of the manuscript as well as the expertise of the reviewers involved. Manuscripts are forwarded for evaluation to Editor-in-Chief (EiC and Section Editors as well as external reviewers to check:
Originality: Submitted manuscript should be original and have the quality to contribute to the respective field of research.
Significance: Results should be interpreted appropriately and significantly. Conclusions must be justified and supported by the results.
Layout and Format: The formatting of the manuscript should be according to the Author Guidelines.
Interest to the Readers: The manuscript should fall within the scope of the journal.
English Level: The English language must be appropriate and understandable.
Overall Merit: Overall benefit of publishing the paper.
Editors/Editorial board members may recommend the acceptance or rejection of a manuscript by conducting the peer-review themselves based on their own knowledge and experience. The Editor-in-Chief(s) may request assistance and advice from other subject matter experts. The peer review is completed once at least two independent reviewers send a detailed report with their comments on the manuscript and their recommendations. The types of decisions are categorized below:
Accept as it is: The manuscript is accepted in its original form. This kind of decision outcome is quite uncommon.
Accept with minor revisions: The paper is accepted for publication after minor modifications or adjustments.
Accept after major revisions: The manuscript is accepted after major amendments. Authors are requested to make major revisions and resolve technique errors, acquire more data, perform a more comprehensive analysis, or even modify the research question to ensure that the manuscript contributes something unique to the body of work.
Revise and resubmit: The journal is willing to reconsider the manuscript in a subsequent round of decision-making provided that the authors make significant revisions to their manuscript.
Reject the manuscript: The manuscript is rejected with no opportunity of resubmission to the journal due to major errors.
The comments of the reviewers are checked by the Editor-in-Chief. The review reports are modified by the Editor-in-Chief if the comments contain sensitive information or are written in a manner that is unsuitable for scholarly communication. This kind of comment should be included in the review form's confidential section, which is only accessible to editors.
Flow Chart of Reviewing Process